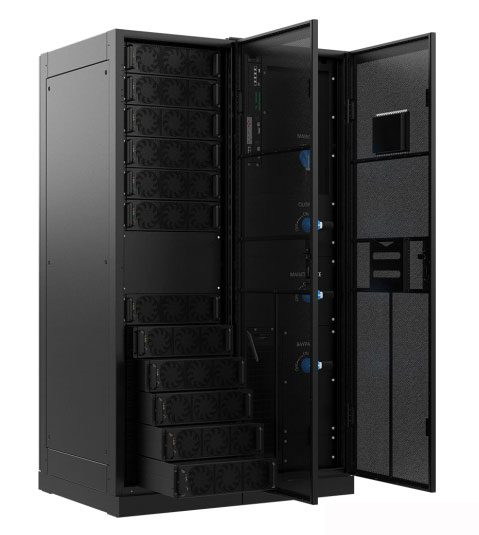
-
What are SNMP and IGBT?
SNMP stands for Simple Network Management Protocol. Its purpose is to enable computers and peripheral devices to connect directly to the network without going through a computer, allowing the network system to manage them. High-end UPSs often have an optional SNMP network management interface that allows the UPS to easily connect to the network.
IGBT stands for Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor. IGBT is a type of power transistor. UPSs designed with this type of transistor can effectively improve product performance, resulting in better power quality, higher efficiency, less heat loss, lower noise, smaller size, and longer product life.
-
What is an isolation transformer?
When using equipment with a general UPS, issues such as interference or malfunction of the equipment often occur due to the zero-to-ground voltage caused by electrical characteristics. To avoid this, some high-end UPSs are designed with isolation transformers. With special design and coordination, the output zero-to-ground voltage can be less than 1V, thus preventing the above issues. Additionally, it has noise filtering functions.
-
What are Boost and Buck?
Boost refers to increasing voltage, while Buck refers to decreasing voltage. When the mains voltage is too low or too high, the voltage stabilizer adjusts the too-low or too-high voltage to the required (or specified) range to enable the UPS or equipment to operate.
-
What is AVR?
AVR stands for Automatic Voltage Regulation. AVR means automatic voltage adjustment, where the UPS adjusts the input voltage through internal output transformer coil turns or power electronic components to achieve a wide mains input range and stable output voltage characteristics.
-
What is Power Factor?
Power Factor is the ratio of actual power consumed to the power supply capacity. Therefore, a higher Power Factor reduces unnecessary losses during power transmission and improves power utilization.
-
How to calculate the power of an uninterruptible power system?
Most uninterruptible power systems (UPS) on the market today are measured in VA (apparent power), where V represents voltage and A represents current. Voltage multiplied by current represents power, which is the capacity of the UPS. For example, a 500VA UPS can supply a current of 4.55A when its output voltage is 110V. If your load requires a current exceeding 4.55A, it is overloaded.
Another unit for power is W, which represents real power. There is a difference between VA and W, where W = VA × cosθ. This cosθ is the Power Factor, which varies among different products, ranging from 0.6 to 0.8. Most commercial products are set at 0.7.
Add up the rated capacity of each load to obtain the total capacity. For loads with high instantaneous startup power consumption, like printers, calculate the instantaneous power consumption separately to avoid overloading when all devices start simultaneously. If the total power consumption (both VA and W) exceeds the UPS output (both VA and W), it is overloaded. In the case of power failure, the UPS may not function properly, putting the load at risk of power interruption.
-
What types of equipment are uninterruptible power systems used for?
Uninterruptible power systems are generally used to protect critical equipment such as computer equipment, precision instruments, medical instruments, etc. Since UPSs are designed primarily for computers, they may not be suitable for all loads, especially inductive loads like electric fans and air conditioners, which can damage offline UPSs due to back electromotive force. Additionally, devices with high instantaneous startup currents, like copiers and laser printers, are not suitable for UPSs due to the risk of overload during simultaneous startup, leading to UPS output interruption in case of power failure. Prolonged overloading of UPSs also shortens the lifespan of electronic components and the UPS itself.
-
The impact of output waveform on loads
Loads are generally classified into three categories: resistive (like light bulbs), capacitive (like switching power supplies), and inductive (like motors). Sine waves are suitable for all three types of loads. Square waves and stepped waves are only suitable for resistive and capacitive loads because the back electromotive force of inductive loads is detrimental to stepped waves. Capacitive loads require higher peak voltages to drive, and square waves and stepped waves have this peak voltage characteristic. However, stepped waves contain harmonic components, which can cause reading errors or malfunctions in some instruments due to harmonic interference.
-
The impact of transfer time on computers
Offline UPS systems have a transfer time during power system conversion. The length of this transfer time varies by manufacturer and typically ranges from 2 to 10 milliseconds. For computers, their switching power supplies can maintain power for 16 milliseconds during power outages, so the transfer time of UPS systems is generally acceptable for personal computers.
-
Why does UPS need to be grounded?
a. On the one hand, it is to protect personal safety and prevent electric shock, and on the other hand, good grounding is conducive to eliminating coupled noise interference.
b. Use a separate grounding method for UPS and computer equipment. The grounding resistance value is recommended to be less than 5Ω. Materials should be of first-grade quality, and construction needs to be strictly required. The grounding point must be far away from the lightning rod grounding point.
-
How to calculate the heat dissipation that UPS should consider?
I. Calculation formula
1-1. BTU/hour = KCal × 3.96
1-2. KCal = KVA × 860
1-3. BTU/hour = KVA (UPS capacity) × 860 × 3.96 × (1 - UPS efficiency)
= KVA (UPS capacity) × 3400 × (1 - UPS efficiency)
II. Example: For a 10KVA UPS with an overall efficiency of 85%, the heat dissipation calculation is as follows:
10KVA × 3400 × (1 - 0.85) = 5100 BTU/hour
-
What is floating charge?
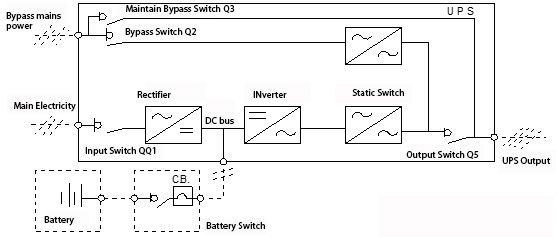
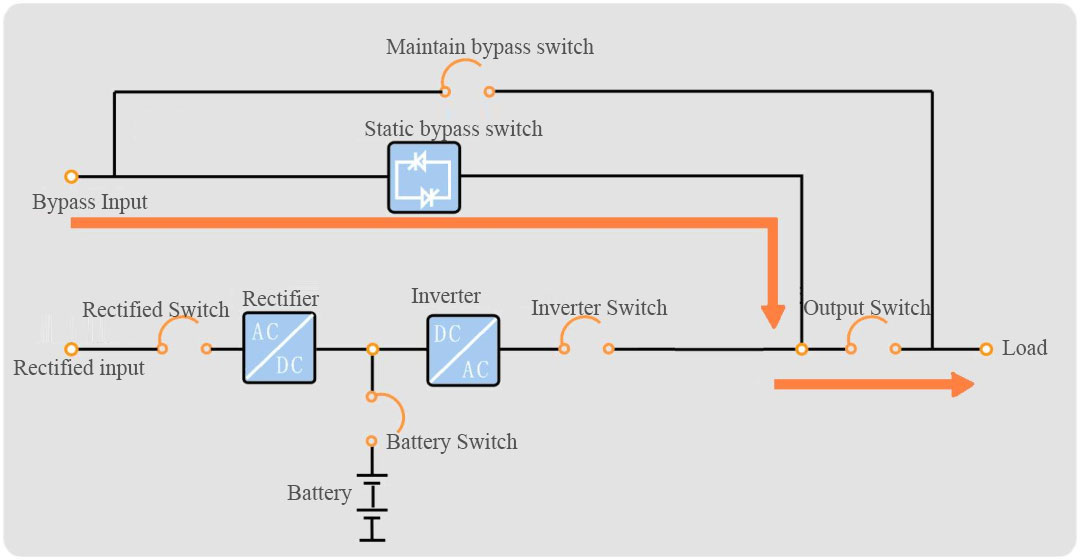 An Offline UPS, as depicted in the block diagram, typically bypasses the mains power directly to the load. Only during a power outage or abnormality does it switch to battery power, which is then converted to AC power by the inverter for the load. Key features:
An Offline UPS, as depicted in the block diagram, typically bypasses the mains power directly to the load. Only during a power outage or abnormality does it switch to battery power, which is then converted to AC power by the inverter for the load. Key features: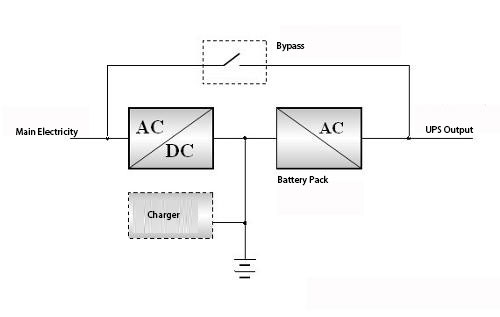 An Online UPS continuously supplies power to the load through its inverter, only switching to bypass mode during UPS faults, overloads, or overheating. Key features:
An Online UPS continuously supplies power to the load through its inverter, only switching to bypass mode during UPS faults, overloads, or overheating. Key features: